Why ROOM Library ?
In android app, We convert raw data into structural data . we use SQLite core library to achieve it .
It handles CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operations required for a database. Java classes and interfaces for SQLite are provided by the android.database. SQLite maintains an effective database management system. But this conventional method has its own disadvantages.
Room provides the abstraction layer over the SQLite DB. ROOM is not a database
It has extended features and ease of use over android SQLite library .
Componentes
There are three main components of Room-

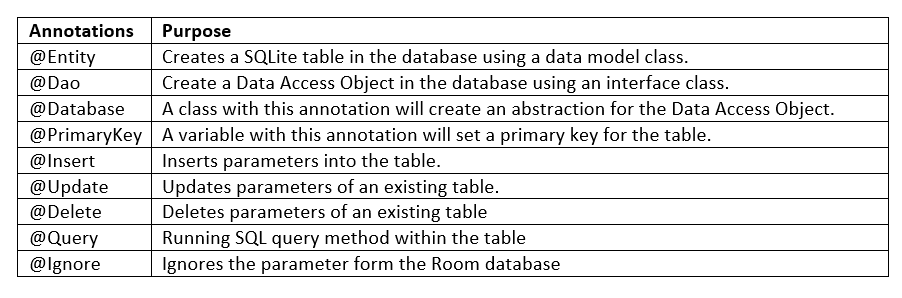
How to Implement?
Before jump into details, Room uses annotations heavily to decrease the boilerplate code.
In android app, We convert raw data into structural data . we use SQLite core library to achieve it .
It handles CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operations required for a database. Java classes and interfaces for SQLite are provided by the android.database. SQLite maintains an effective database management system. But this conventional method has its own disadvantages.
- You have to write long repetitive code, which will be time-consuming as well as prone to mistakes.
- Syntax errors in queries
- No compile time error detection (Time consuming)
- Parsing is required to convert data to Plain Old Java Objects (POJO) objects
- It is very difficult to manage SQL queries for a complex relational database.
What is ROOM?
Room provides the abstraction layer over the SQLite DB. ROOM is not a databaseIt has extended features and ease of use over android SQLite library .
Componentes
There are three main components of Room-
- Database: Contains the database holder and serves as the main access point for the underlying connection to your app's persisted, relational data.The class that's annotated with
@Databaseshould satisfy the following conditions:- Be an abstract class that extends
RoomDatabase. - Include the list of entities associated with the database within the annotation.
- Contain an abstract method that has 0 arguments and returns the class that is annotated with
@Dao.
At runtime, you can acquire an instance ofDatabaseby callingRoom.databaseBuilder()orRoom.inMemoryDatabaseBuilder(). - Be an abstract class that extends
- Entity: Represents a table within the database.
- tableName attribute is used to define the name of the table
- Every entity class must have at-least one Primary Key field, annotated with @PrimaryKey
- Fields in entity class can be annotated with @ColumnInfo(name = “name_of_column”) annotation to give specific column names
- DAO: Contains the methods used for accessing the database.
- Data Access Object is either be an interface or an abstract class annotated with
@Doaannotation, containing all the methods to define the operations to be performed on data. The methods can be annotated with

How to Implement?
Before jump into details, Room uses annotations heavily to decrease the boilerplate code.




No comments:
Post a Comment